Microservices on Kubernetes EKS - Complete Deployment Guide



A comprehensive hands-on guide for deploying a production-ready microservices application on AWS EKS using modern DevOps practices.
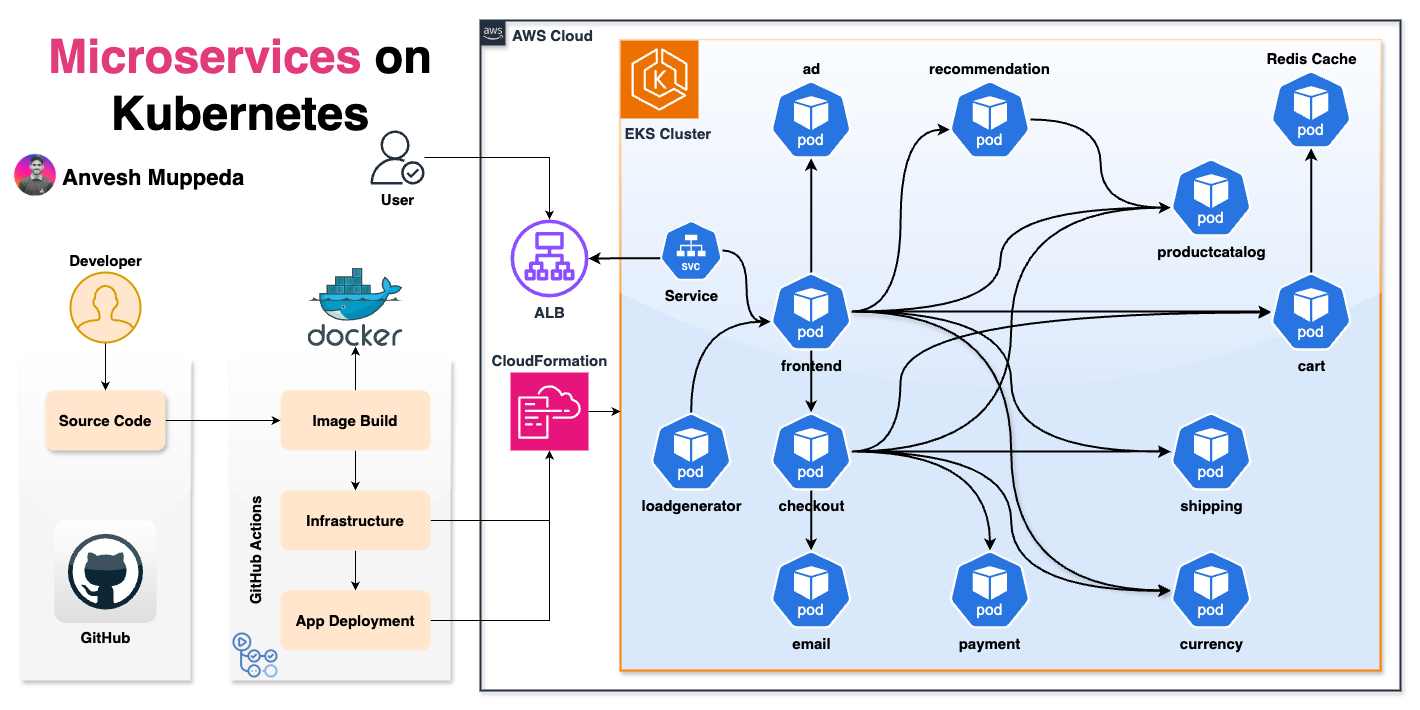
🏗️ Architecture Overview
This project demonstrates a complete microservices architecture deployed on AWS EKS, featuring:
- 11 Microservices: Ad, Recommendation, Product Catalog, Cart, Shipping, Currency, Payment, Email, Checkout, Load Generator, and Frontend
- AWS EKS Cluster: Managed Kubernetes service for container orchestration
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): For traffic routing and load balancing
- Redis Cache: For session management and caching
- CloudFormation: Infrastructure as Code for AWS resource provisioning
- GitHub Actions: Automated CI/CD pipeline
- Docker Hub: Container image registry
📁 Project Structure
├── infrastructure/ # AWS CloudFormation templates
│ └── microservice-demo-cft.yaml
├── helm-charts/ # Helm charts for application deployment
│ └── microservices-demo/
├── kubernetes-manifests/ # Raw Kubernetes YAML manifests
├── src/ # Source code for all microservices
├── .github/workflows/ # GitHub Actions CI/CD pipelines
└── kustomization.yaml # Kustomize configuration
🚀 Quick Start Guide
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following tools installed:
- AWS CLI (v2.0+)
- kubectl (compatible with your EKS cluster version)
- Docker (for local testing)
- Helm (v3.0+)
- Git
Step 1: Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/anveshmuppeda/kubernetes.git
cd kubernetes/projects/microservices-project
Step 2: Deploy Complete Infrastructure & Application
You have two options for deployment:
Option A: Complete Automated Deployment (Recommended)
Single-Command Full Stack Deployment using GitHub Actions:
-
Navigate to GitHub Actions in your repository
-
Select "Deploy Microservices Demo Infra & Helm Chart to EKS Cluster" workflow
-
Click "Run workflow" and configure parameters:
- Stack Name:
microservices-demo-eks(default) - EKS Cluster Name:
microservices-demo-cluster(default) - Desired Node Size:
2(default) - AWS Region: Select from
us-east-1,us-east-2, orus-west-2
- Stack Name:
-
Monitor the workflow execution:
- Phase 1: Infrastructure deployment (15-20 minutes)
- Phase 2: Application deployment via Helm (5-10 minutes)
- Total Time: ~25-30 minutes for complete stack
This workflow will:
✅ Deploy EKS cluster with CloudFormation
✅ Configure kubectl access
✅ Install Helm charts
✅ Deploy all microservices
✅ Set up load balancers and networking
Option B: Manual Step-by-Step Deployment
# Step 1: Configure AWS Credentials
aws configure
# Step 2: Deploy EKS Cluster using CloudFormation
cd infrastructure
aws cloudformation deploy \
--region us-east-1 \
--stack-name microservices-demo-eks \
--template-file microservice-demo-cft.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND \
--parameter-overrides \
EksClusterName=microservices-demo-cluster \
DesiredSize=2
# Step 3: Update kubeconfig
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region us-east-1 --name microservices-demo-cluster
# Step 4: Deploy applications with Helm
helm upgrade --install microservice-demo \
helm-charts/microservices-demo \
--namespace microservices --create-namespace
Update kubeconfig
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region <your-region> --name microservices-demo-cluster
Step 3: Verify Complete Deployment
After the automated deployment completes, verify everything is running:
# Check cluster status
kubectl get nodes
# Verify all pods are running
kubectl get pods -n microservices
# Check services and load balancers
kubectl get svc -n microservices
# Get the application URL
kubectl get ingress -n microservices
Step 4: Access Your Application
Once deployment is complete, your microservices application will be accessible via the Application Load Balancer URL provided in the ingress output.
Step 5: Set Up GitHub Actions Secrets (One-Time Setup)
Navigate to your GitHub repository and add the following secrets:
| Secret Name | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID | AWS Access Key for EKS deployment | AKIAXXXXX |
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | AWS Secret Key | xxxxx |
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME | Your Docker Hub username | anveshmuppeda |
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN | Docker Hub access token | dckr_pat_xxxxx |
Step 6: Deploy Applications (Alternative Methods)
If you prefer manual deployment after infrastructure is ready:
Option A: Using Helm Charts (Automated in main workflow)
cd helm-charts
# Install the microservices application
helm upgrade --install microservice-demo \
microservices-demo \
--namespace microservices \
--create-namespace
Option B: Using Kubernetes Manifests
cd kubernetes-manifests
# Apply all manifests
kubectl apply -f .
Option C: Using Kustomize
# Deploy using Kustomize
kubectl apply -k .
Step 6: Verify Deployment
# Check all pods are running
kubectl get pods -n microservices
# Check services
kubectl get svc -n microservices
# Get the Load Balancer URL
kubectl get ingress -n microservices
🔄 CI/CD Pipeline Overview
This project features three main GitHub Actions workflows for complete automation:
1. Complete Infrastructure & Application Pipeline (Primary)
Workflow: Deploy Microservices Demo Infra & Helm Chart to EKS Cluster
Purpose: End-to-end deployment from infrastructure to running application
Triggers: Manual workflow dispatch with customizable parameters
Two-Job Architecture:
Job 1: Infrastructure Deployment (deploy-cft)
- Duration: ~15-20 minutes
- Purpose: Provisions AWS EKS cluster using CloudFormation
- Features:
- Flexible configuration (stack name, cluster name, node size, region)
- Multi-region support (
us-east-1,us-east-2,us-west-2) - Scalable node groups (configurable desired size)
- IAM capabilities for complex permissions
Job 2: Application Deployment (deploy-helm)
- Duration: ~5-10 minutes
- Purpose: Deploys all microservices using Helm charts
- Dependencies: Waits for infrastructure job completion
- Features:
- Automatic kubectl configuration
- Helm chart installation
- Namespace creation and management
- Service mesh deployment
Complete Deployment Flow:
graph TD
A[Trigger Workflow] --> B[Deploy CloudFormation]
B --> C[EKS Cluster Ready]
C --> D[Configure kubectl]
D --> E[Install Helm]
E --> F[Deploy Helm Charts]
F --> G[All Services Running]
G --> H[Application Accessible]
2. Infrastructure-Only Pipeline
Workflow: Deploy Microservices Demo EKS Cluster using CFT
Purpose: Infrastructure provisioning only (for advanced users)
3. Application Build Pipeline
Workflow: MicroServices Demo | AdService - Docker Build
Purpose: Container image building and publishing
Automated Build Process:
-
Triggers on:
- Manual dispatch with version bump selection
- Push to
mainorfeature/microservicesdemobranches - Changes to Dockerfile paths
-
Version Management:
- Fetches latest version from Docker Hub
- Calculates new version based on semantic versioning
- Supports major, minor, and patch bumps
-
Build Process:
- Multi-architecture builds (AMD64 and ARM64)
- Pushes to Docker Hub with version tags
- Updates both
latestand versioned tags
Pipeline Workflow Sequence
graph LR
A[Code Push] --> B[Infrastructure Pipeline]
B --> C[EKS Cluster Ready]
C --> D[Application Pipeline]
D --> E[Docker Images Built]
E --> F[Deploy to EKS]
F --> G[Application Running]
Required GitHub Secrets
| Secret Name | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID | AWS Access Key for EKS deployment | Infrastructure Pipeline |
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | AWS Secret Key | Infrastructure Pipeline |
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME | Docker Hub username | Application Pipeline |
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN | Docker Hub access token | Application Pipeline |
Manual Trigger Examples
# Complete Infrastructure + Application Deployment (Recommended)
gh workflow run "Deploy Microservices Demo Infra & Helm Chart to EKS Cluster" \
--field stack-name="production-microservices" \
--field EksClusterName="prod-cluster" \
--field DesiredSize="4" \
--field region="us-west-2"
# Infrastructure Only
gh workflow run "Deploy Microservices Demo EKS Cluster using CFT" \
--field stack-name="staging-infrastructure" \
--field EksClusterName="staging-cluster" \
--field DesiredSize="2" \
--field region="us-east-1"
# Application Build
gh workflow run "MicroServices Demo | AdService - Docker Build" \
--field bump-type=minor
# Instead of AdService, you can specify any service like `frontend`, `cartservice`, etc.
Deployment Timeline
| Phase | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | 15-20 min | EKS cluster, VPC, security groups, node groups |
| Application | 5-10 min | Helm chart deployment, pod startup, load balancer |
| Total | 20-30 min | Complete working application |
🛠️ Service Details
Core Services
| Service | Purpose | Port | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| frontend | Web UI | 8080 | Go |
| adservice | Ad recommendations | 9555 | Java |
| cartservice | Shopping cart | 7070 | C# |
| checkoutservice | Order processing | 5050 | Go |
| currencyservice | Currency conversion | 7000 | Node.js |
| emailservice | Email notifications | 8080 | Python |
| paymentservice | Payment processing | 50051 | Node.js |
| productcatalogservice | Product catalog | 3550 | Go |
| recommendationservice | ML recommendations | 8080 | Python |
| shippingservice | Shipping quotes | 50051 | Go |
Supporting Services
| Service | Purpose | Port |
|---|---|---|
| redis-cart | Cart session storage | 6379 |
| loadgenerator | Traffic simulation | - |
🔧 Configuration Management
Environment Variables
Key environment variables for each service:
# Frontend Service
- PORT: "8080"
- PRODUCT_CATALOG_SERVICE_ADDR: "productcatalogservice:3550"
- CURRENCY_SERVICE_ADDR: "currencyservice:7000"
- CART_SERVICE_ADDR: "cartservice:7070"
# Cart Service
- REDIS_ADDR: "redis-cart:6379"
- PORT: "7070"
# Checkout Service
- PRODUCT_CATALOG_SERVICE_ADDR: "productcatalogservice:3550"
- SHIPPING_SERVICE_ADDR: "shippingservice:50051"
- PAYMENT_SERVICE_ADDR: "paymentservice:50051"
Resource Requirements
Recommended resource allocations:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 64Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 128Mi
📊 Monitoring and Observability
Health Checks
Each service includes health check endpoints:
# Check service health
kubectl get pods -n microservices
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n microservices
Logs
View service logs:
# View logs for a specific service
kubectl logs -f deployment/frontend -n microservices
# View logs with timestamp
kubectl logs --timestamps deployment/cartservice -n microservices
🔒 Security Considerations
Network Policies
Implement network policies to restrict pod-to-pod communication:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: microservices-netpol
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
Service Accounts
Each service runs with minimal required permissions using dedicated service accounts.
📈 Scaling and Performance
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
Enable autoscaling for services:
kubectl autoscale deployment frontend --cpu-percent=70 --min=2 --max=10 -n microservices
Load Testing
The included load generator creates realistic traffic:
# Check load generator status
kubectl logs deployment/loadgenerator -n microservices
🐛 Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Pods stuck in Pending state:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n microservices
# Check events section for resource constraints
Service connectivity issues:
# Test service connectivity
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -n microservices -- nslookup productcatalogservice
Load Balancer not accessible:
# Check ALB controller logs
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment/aws-load-balancer-controller
Debug Commands
# Get all resources
kubectl get all -n microservices
# Check ingress status
kubectl describe ingress -n microservices
# View cluster events
kubectl get events -n microservices --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp
🔄 Updates and Maintenance
Rolling Updates
Update a service image:
kubectl set image deployment/frontend frontend=anveshmuppeda/microservices-demo-frontend:v1.2.3 -n microservices
Backup Strategies
Regular backup of:
- EKS cluster configuration
- Application configurations
- Persistent volume data
📚 Additional Resources
Related Documentation
Useful Commands Cheat Sheet
# Cluster Management
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
kubectl top nodes
# Application Management
kubectl get pods -o wide
kubectl get svc
kubectl get ingress
# Scaling
kubectl scale deployment frontend --replicas=3
kubectl get hpa
# Logs and Debugging
kubectl logs -f <pod-name>
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/sh
kubectl port-forward svc/frontend 8080:8080
🤝 Contributing
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/awesome-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add awesome feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/awesome-feature) - Open a Pull Request
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
👨💻 Author
Anvesh Muppeda
- GitHub: @anveshmuppeda
- Docker Hub: anveshmuppeda
Happy Deploying! 🚀
For questions or support, please open an issue in the GitHub repository.
