A Hands-On Guide to AWS EKS Fargate Cluster
Deploy Serverless Containers on EKS with Fargate Profiles – Step-by-Step Tutorial
Medium Blog Link: ⎈ Hands-On Guide to Creating an Amazon EKS Cluster with Self-Managed Worker Nodes ⎈
Introduction
AWS Fargate eliminates the need to manage EC2 instances for Kubernetes workloads, allowing you to focus on applications instead of infrastructure. In this guide, you’ll learn to:
- Create an EKS cluster.
- Configure Fargate profiles to run serverless pods.
- Deploy and troubleshoot applications on Fargate.
Prerequisites
- AWS CLI: Installed and configured (
aws configure). - kubectl: Installed (guide).
- IAM Permissions: Ability to create EKS clusters, IAM roles, and Fargate profiles.
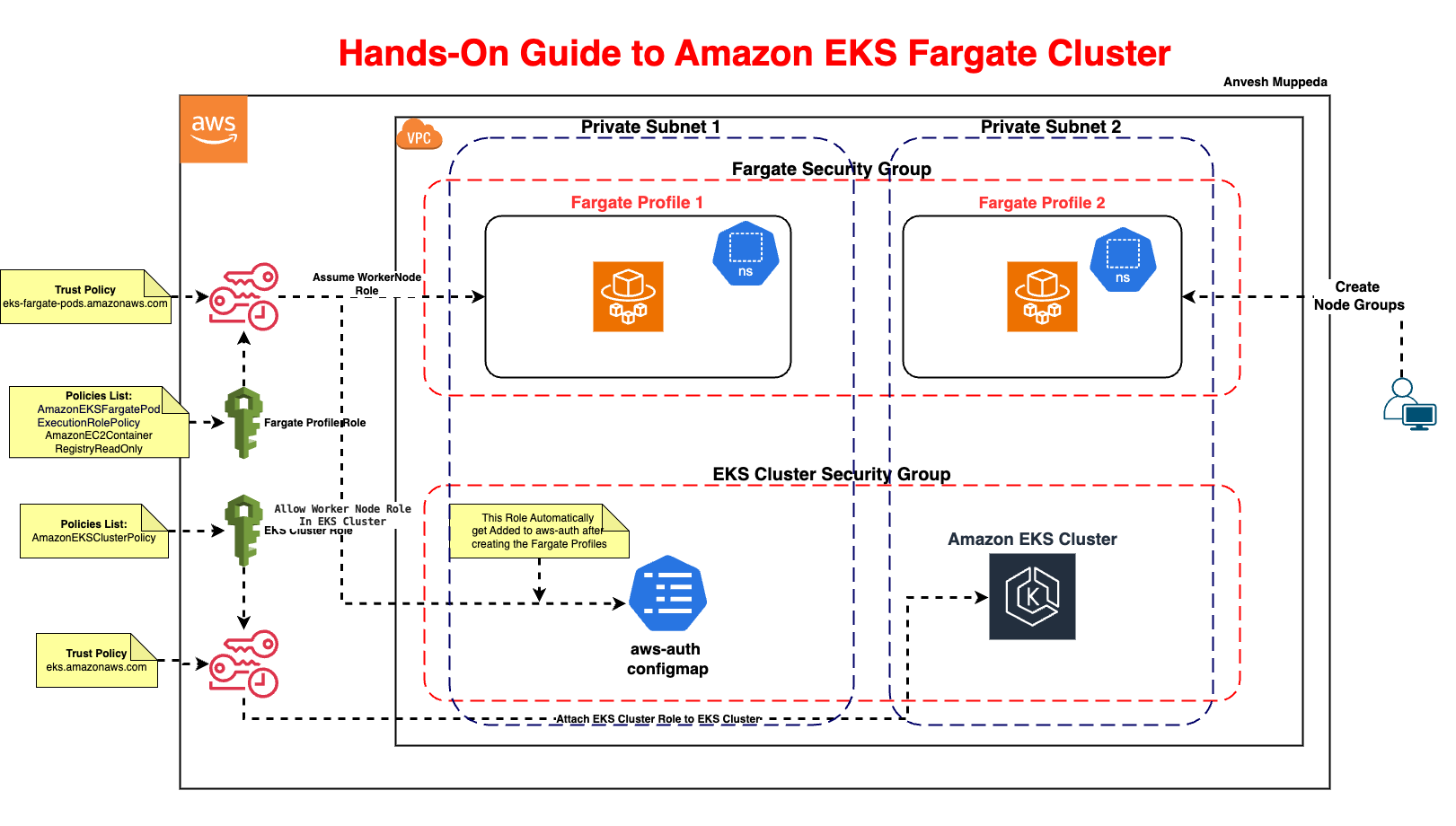
Step 1: Create IAM Roles
1.1 EKS Cluster Role
Fargate requires the same cluster role as standard EKS.
a. Trust Policy (cluster-trust-policy.json)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": { "Service": "eks.amazonaws.com" },
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
b. Create and Attach Policy
aws iam create-role \
--role-name EKSFargateClusterRole \
--assume-role-policy-document file://cluster-trust-policy.json
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name EKSFargateClusterRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
1.2 Fargate Execution Role
Pods running on Fargate need permissions to pull images and write logs.
a. Trust Policy (fargate-trust-policy.json)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": { "Service": "eks-fargate-pods.amazonaws.com" },
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
b. Create and Attach Policies
aws iam create-role \
--role-name EKSFargatePodExecutionRole \
--assume-role-policy-document file://fargate-trust-policy.json
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name EKSFargatePodExecutionRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSFargatePodExecutionRolePolicy
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name EKSFargatePodExecutionRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly
Step 2: Create the EKS Cluster
aws eks create-cluster \
--name FargateEKSClusterDemo \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:role/EKSFargateClusterRole \
--resources-vpc-config subnetIds=subnet-12345678,subnet-87654321
Wait for cluster activation (10–15 minutes):
aws eks describe-cluster --name FargateEKSClusterDemo --query "cluster.status"
Step 3: Configure kubectl
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name FargateEKSClusterDemo --region us-east-1
Step 4: Create a Fargate Profile
Fargate profiles define which pods run on Fargate based on namespaces and labels.
The following create-fargate-profile example creates an EKS Fargate Profile for a selector with a namespace.
# General Command
aws eks create-fargate-profile \
--cluster-name <cluster-name> \
--fargate-profile-name demo-fargate-profile \
--pod-execution-role-arn arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:role/EKSFargatePodExecutionRole \
--subnets subnet-12345678 subnet-87654321 \ # Make sure the subnets are private
--selectors '{"namespace": "<namespace-name>"}' # Target pods in this namespace
# Example
aws eks create-fargate-profile \
--cluster-name FargateEKSClusterDemo \
--fargate-profile-name demo-fargate-profile \
--pod-execution-role-arn arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/EKSFargatePodExecutionRole \
--subnets subnet-1234567890 \
--selectors '[{"namespace": "fargate-ns"},{"namespace": "kube-system"}]' # Target pods in this namespace
Key Parameters:
--selectors: Specify namespaces or labels to schedule pods on Fargate.--subnets: Use private subnets for fargate workloads.
Wait for profile activation (2–5 minutes):
aws eks describe-fargate-profile \
--cluster-name FargateEKSClusterDemo \
--fargate-profile-name my-fargate-profile \
--query "fargateProfile.status"
Step 5: Deploy a Sample Application
5.1 Create a Namespace
kubectl create ns fargate-ns # Must match the Fargate profile selector
5.2 Deploy an Nginx Pod
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: fargate-ns
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOF
5.3 Verify Pods Are Running on Fargate
kubectl get pods -n fargate-ns -o wide
Output:
NAME READY STATUS IP NODE AGE
nginx-abcde 1/1 Running 192.168.1.100 fargate-ip-192-168-1-100.ec2.internal 1m
Troubleshooting Fargate Issues
1. Pods Stuck in Pending State
-
Check Fargate Profile Status:
aws eks describe-fargate-profile --cluster-name FargateEKSClusterDemo --fargate-profile-name my-fargate-profileEnsure the profile is
ACTIVE. -
Verify Namespace Selectors: The pod’s namespace must match the Fargate profile selector.
2. Permission Errors
- Pod Execution Role: Ensure the role has
AmazonEKSFargatePodExecutionRolePolicyandAmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly.aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name EKSFargatePodExecutionRole
3. Networking Issues
- Subnet Tags: Ensure subnets are tagged for EKS:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources subnet-12345678 --tags Key=kubernetes.io/cluster/FargateEKSClusterDemo,Value=shared
Cleanup
-
Delete the Fargate Profile:
aws eks delete-fargate-profile \
--cluster-name FargateEKSClusterDemo \
--fargate-profile-name my-fargate-profile -
Delete the EKS Cluster:
aws eks delete-cluster --name FargateEKSClusterDemo -
Delete IAM Roles:
aws iam delete-role --role-name EKSFargateClusterRole
aws iam delete-role --role-name EKSFargatePodExecutionRole
Best Practices for EKS Fargate
- Namespace Strategy: Use dedicated namespaces (e.g.,
prod-fargate,dev-fargate) to isolate workloads. - Cost Optimization:
- Use Spot capacity for non-critical workloads (Fargate Spot).
- Monitor costs with AWS Cost Explorer.
- Logging: Integrate with AWS CloudWatch for centralized logging.
- Security:
- Restrict pod execution roles using IAM policies.
- Use private subnets for internal workloads.
Fargate vs. Managed Node Groups
| Feature | Fargate | Managed Node Groups |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Serverless (no nodes to manage) | EC2 instances managed by AWS |
| Pricing | Per vCPU/memory/hour | Per EC2 instance + EKS fee |
| Use Cases | Microservices, batch jobs | Stateful apps, GPU workloads |
| Scaling | Automatic (per pod) | Managed by Cluster Autoscaler |
Conclusion
AWS EKS Fargate simplifies Kubernetes by abstracting infrastructure management. By following this guide, you’ve learned to:
- Deploy a serverless EKS cluster.
- Schedule pods on Fargate using profiles.
- Troubleshoot common issues like pending pods.
Next Steps:
- Explore Fargate Spot for cost savings.
- Set up AWS App Mesh for service mesh on Fargate.
Need help? Ask in the comments! 🚀
Additional Resources: