Hands-On Guide to Creating an Amazon EKS Cluster with Managed Node Groups
Simplify Kubernetes Operations with AWS-Managed Worker Nodes
Medium Blog Link: ⎈ Hands-On Guide to Creating an Amazon EKS Cluster with Managed Node Groups ⎈
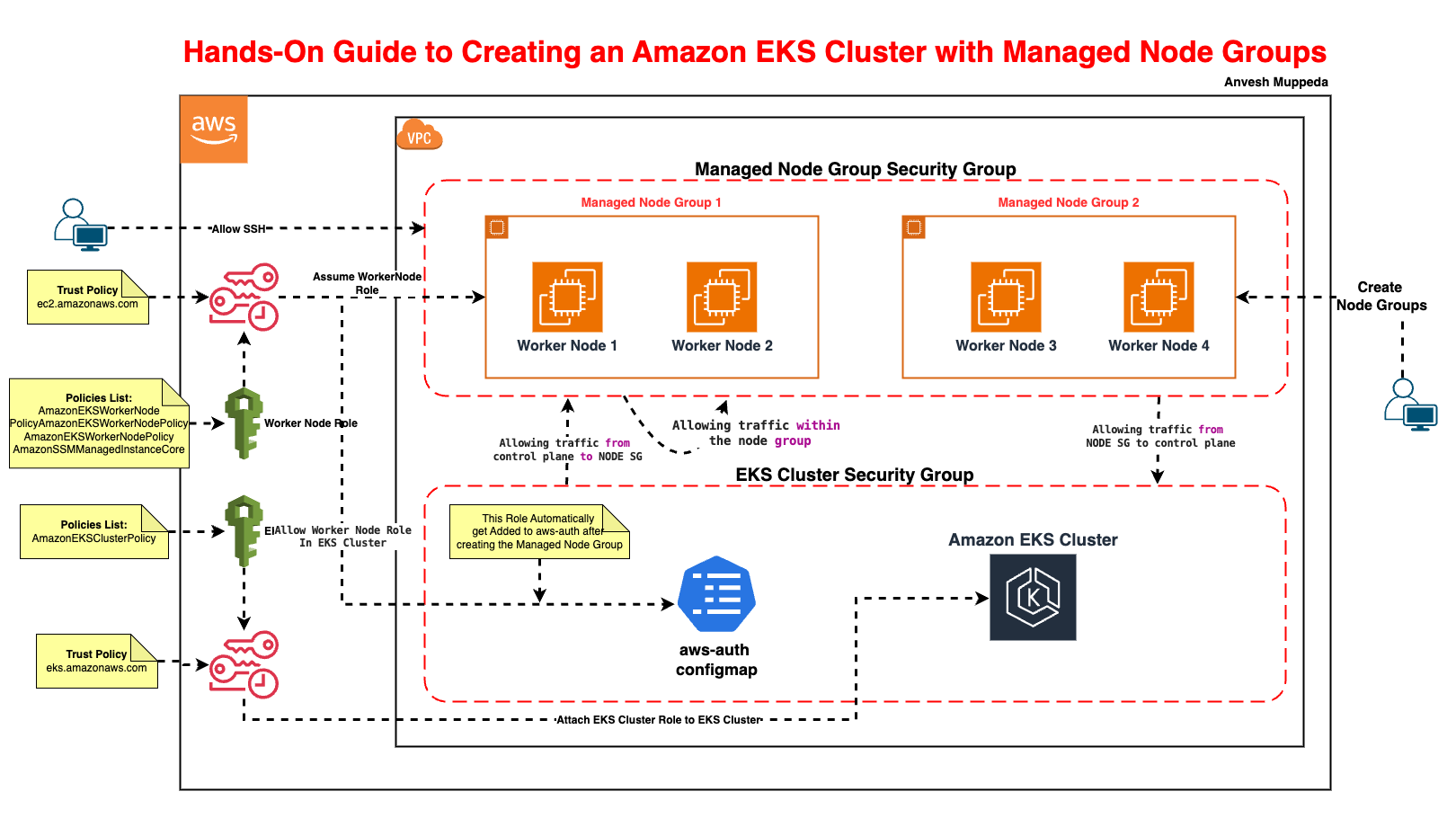
Introduction
Amazon EKS Managed Node Groups automate the provisioning, scaling, and lifecycle management of worker nodes, reducing operational overhead.
In this guide, you’ll learn to:
- Create an EKS cluster.
- Deploy Managed Worker Node Group.
Prerequisites
- AWS CLI: Installed and configured with
aws configure. - kubectl: For interacting with Kubernetes (installation guide).
- Basic AWS Knowledge: Familiarity with IAM, VPC, and EC2.
Step 1: Create an IAM Role for the EKS Cluster
Why? The EKS control plane needs permissions to manage AWS resources.
-
Create a trust policy file (
cluster-trust-policy.json):{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": { "Service": "eks.amazonaws.com" },
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}Explanation: This allows the EKS service to assume the role.
-
Create the IAM role:
# General Command
aws iam create-role \
--role-name <Cluster-Role-Name> \
--assume-role-policy-document file://cluster-trust-policy.json
# Example
aws iam create-role \
--role-name ManagedEKSClusterRole \
--assume-role-policy-document file://cluster-trust-policy.json -
Attach the EKS cluster policy:
# General Command
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name <Cluster-Role-Name> \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
# Example
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name ManagedEKSClusterRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
Step 2: Create the EKS Cluster
Why? The cluster is the Kubernetes control plane managed by AWS.
-
Run the cluster creation command:
# General Command
aws eks create-cluster \
--name <Cluster-Name> \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::<AWS-Account-ID>:role/<Cluster-Role-Name> \
--resources-vpc-config subnetIds=<Subnet-ID-1>,<Subnet-ID-2>
# Example
aws eks create-cluster \
--name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/ManagedEKSClusterRole \
--resources-vpc-config subnetIds=subnet-12345678,subnet-12345678- Replace
<AWS-Account-ID>with your account ID (find it viaaws sts get-caller-identity). - Use public subnets from your VPC.
- Replace
-
Wait for the cluster to activate (10-15 mins):
aws eks describe-cluster --name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo --query "cluster.status"Expected Output:
"ACTIVE".
Step 3: Configure kubectl to Access the Cluster
Why? To interact with the cluster using kubectl.
-
Update kubeconfig:
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo --region us-east-1 -
Verify access:
kubectl get nodesOutput:
No resources found(no nodes yet).
Step 4: Create an IAM Role for Worker Nodes
Why? Nodes need permissions to join the cluster and pull container images.
-
Create a node trust policy file (
node-trust-policy.json):{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": { "Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com" },
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
} -
Create the IAM role:
# General Command
aws iam create-role \
--role-name <Node-Role-Name> \
--assume-role-policy-document file://node-trust-policy.json
# Example
aws iam create-role \
--role-name ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole \
--assume-role-policy-document file://node-trust-policy.json -
Attach required policies:
# Attach worker node policy
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy
# Attach CNI policy (for networking)
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
# Attach ECR read-only access
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly
Step 5: Launch Managed Worker Nodes
Why? Worker nodes run your Kubernetes pods.
- Create an Cluster Node Group:
Or you can use eksctl as well, to create cluster and node groups
# General Command
> aws eks create-nodegroup \
--cluster-name <EKS Cluster Name> \
--nodegroup-name <NodeGroupName>> \
--scaling-config minSize=1,maxSize=2,desiredSize=1 \
--subnets <Subnet-ID-1>,<Subnet-ID-2> \
--node-role arn:aws:iam::<account-id>:role/<nodegroup role name> \
--remote-access ec2SshKey=<SSH Key Name> \
--instance-types <Instance Type>> \
--ami-type <AMI Type> \
--capacity-type ON_DEMAND|Spot \
--update-config maxUnavailable=1 \
--labels node.kubernetes.io/scope=system \
--tags <Key>=<Value>
# Example
aws eks create-nodegroup \
--cluster-name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo \
--nodegroup-name MangedWorkerNodeGroup \
--scaling-config minSize=1,maxSize=2,desiredSize=1 \
--subnets subnet-12345678 subnet-12345678 \
--node-role arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole \
--remote-access ec2SshKey=eksWorkerKey \
--instance-types t3.medium \
--ami-type AL2_x86_64 \
--capacity-type ON_DEMAND \
--update-config maxUnavailable=1 \
--labels node.kubernetes.io/scope=system \
--tags Application=ManagedNodeGroupApp
Step 6: Verify Node Group Status
Why? Nodes need RBAC permissions to register with the control plane.
- Verify the
aws-authConfigMap:
Above node group creation command automatically added our Worker Node Role to aws-auth configmap since it is eks managed worker node group.
> kubectl get cm aws-auth -n kube-system -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
mapRoles: |
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
rolearn: arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2025-02-24T00:17:04Z"
name: aws-auth
namespace: kube-system
resourceVersion: "5156"
uid: 5ef2e2d0-a9bc-4344-9441-d6c7c95e6a93
- Verify nodes join the cluster:
Expected Output:
kubectl get nodesNAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-1-1.ec2.internal Ready <none> 2m v1.30.0-eks-xxxxxxx
Troubleshooting
- Node Group Fails to Create IAM Permissions: Ensure the node role has AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy, AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly, and AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy.
Subnets: Use private subnets if nodes don’t need public IPs.
- Nodes Not Joining the Cluster Check aws-auth ConfigMap (auto-created for managed node groups):
kubectl describe configmap aws-auth -n kube-system
Security Groups: Ensure nodes can communicate with the EKS API (port 443).
- SSH Access Issues Ensure the key pair (my-keypair) exists in your AWS region.
Cleanup
Avoid unnecessary charges by deleting resources:
# Delete the EKS cluster
aws eks delete-cluster --name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo
# Delete the Node Group
aws eks delete-nodegroup --nodegroup-name MangedWorkerNodeGroup --cluster-name Manged-EKS-Cluster-Demo
# Delete IAM roles
aws iam delete-role --role-name ManagedEKSClusterRole
aws iam delete-role --role-name ManagedEKSNodeGroupRole
Conclusion
Managed node groups simplify Kubernetes operations by automating node provisioning, scaling, and updates. By following this guide, you’ve learned to:
- Create an EKS cluster.
- Deploy managed nodes with AWS-optimized configurations.
- Troubleshoot common issues.
You’ve successfully created an EKS cluster with self-managed worker nodes! Key takeaways:
- IAM Roles: Ensure correct trust policies and permissions.
- Security Groups: Configure inbound/outbound rules properly.
aws-authConfigMap: Critical for node authentication.
Next Steps:
Explore EKS Add-ons for logging, monitoring, and security.
Configure Cluster Autoscaler for dynamic scaling.
Got questions or facing issues? Let me know in the comments! 👇
Additional Resources: