Welcome to Kubernetes Hands-On Guides
Welcome to the Kubernetes Hands-On Guides! This project is your one-stop resource for mastering Kubernetes with practical examples, tutorials, and tools. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced user, you'll find valuable content to enhance your Kubernetes knowledge.
Getting Started
Start your Kubernetes journey by exploring our comprehensive guides and tutorials. These resources are designed to help you set up, manage, and optimize Kubernetes clusters effectively.
Why These Guides? 💡
✅ Battle-Tested Content - Lessons from managing 1000+ pods in production
✅ Cloud-Agnostic - Works on AWS EKS, GCP GKE, Azure AKS, and bare metal
✅ Version Current - Updated for Kubernetes 1.32+ features
✅ Zero Fluff - Direct executable examples with explanations
✅ Hands-On - Practical exercises to reinforce learning
✅ Open Source - Contribute to the community and share your knowledge
✅ Multi-Cloud - Works on AWS EKS, GCP GKE, Azure AKS, and bare metal
✅ Zero Fluff - Direct executable examples with explanations
Architecture
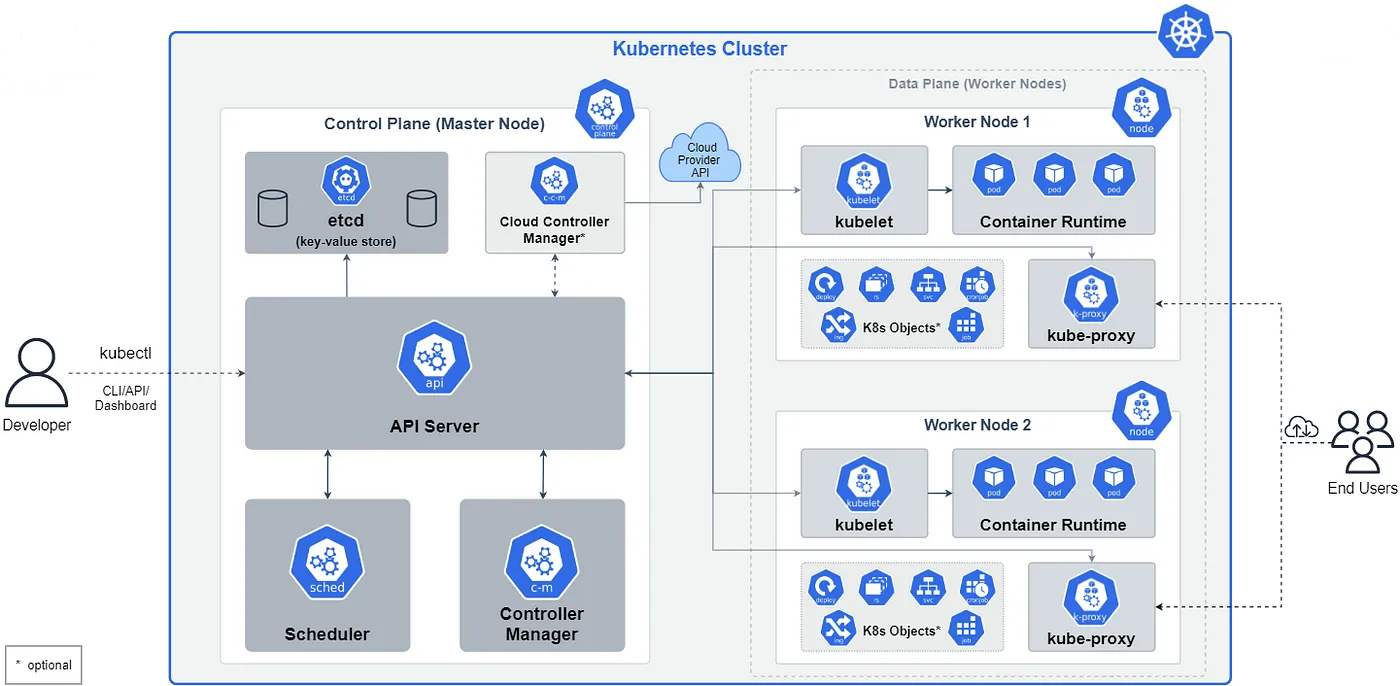
Master Node Components
The master node is responsible for managing the Kubernetes cluster. It oversees the nodes and the pods running within the cluster. Key components of the master node include:
- API Server: Exposes the Kubernetes API, acting as the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
- Etcd: A consistent and highly-available key-value store used for all cluster data.
- Scheduler: Assigns workloads to the worker nodes based on resource availability.
- Controller Manager: Runs controller processes to regulate the state of the cluster, handling tasks like node failures and endpoint management.
- Cloud Controller Manager: Manages cloud-specific controller processes.
Worker Node Components
Worker nodes run the applications and handle the containerized workloads. Each worker node has its own set of components:
- Kubelet: Ensures that containers are running in a pod by communicating with the master node.
- Kube-proxy: Maintains network rules and handles network communication within and outside the cluster.
- Container Runtime: Runs the containers. Common runtimes include Docker, containerd, and CRI-O.
📚 Guides Covered in This Repository
This repository contains a comprehensive set of hands-on guides and practical examples for mastering Kubernetes. Below is a categorized list of topics covered:
Kubernetes Basics
- Introduction to Kubernetes Architecture
- Understanding Master and Worker Node Components
- Pods, Services, and Deployments
- Namespaces and Resource Management
- Volumes and Persistent Storage
Advanced Kubernetes Concepts
- Rolling Updates and Recreate Deployment Strategies
- Blue-Green and Canary Deployment Strategies
- Kubernetes RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)
- Kubernetes Resource Quotas and Limit Ranges
- Kubernetes Pod Disruption Budgets (PDBs)
Kubernetes Tools
- Using
kubectlfor Cluster Management - Helm: Kubernetes Package Manager
- Velero: Backup and Restore for Kubernetes
- ArgoCD: Continuous Delivery for Kubernetes
- FluxCD: GitOps for Kubernetes
- eksctl: Managing Amazon EKS Clusters
Kubernetes Networking
- Kubernetes Ingress and Routing
- Transitioning to HTTPS with Self-Signed Certificates
- Kubernetes Taints and Tolerations
- Kubernetes Endpoints and EndpointSlices
- Kubernetes Network Policies
- Kubernetes Service Mesh (Istio, Linkerd)
- Kubernetes Load Balancing and Ingress Controllers
- Kubernetes DNS and CoreDNS
- Kubernetes Network Troubleshooting
- Kubernetes Network Performance Optimization
- Kubernetes Network Security Best Practices
- Kubernetes Network Monitoring and Logging
- Kubernetes Network Policy Examples
- Kubernetes Network Policy Best Practices
- Kubernetes Network Policy Troubleshooting
- Kubernetes Network Policy Use Cases
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Istio
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Linkerd
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Calico
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Cilium
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Weave Net
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Flannel
- Kubernetes Network Policy with Kube-router
Kubernetes Scaling and Performance
- Horizontal and Vertical Pod Autoscalers
- Kubernetes Priority Classes and QoS Classes
- Scaling with Karpenter on AWS EKS
Kubernetes on Cloud
- Setting Up Amazon EKS Clusters with eksctl
- Using Fargate Profiles in Amazon EKS
- Azure DevOps Self-Hosted Agents on Kubernetes
🚀 How to Use This Repository Effectively
1. Clone the Repository
Start by cloning the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/anveshmuppeda/kubernetes.git
cd kubernetes
2. Explore the Guides
The repository is organized into directories and files for each topic. Navigate through the folders to find the guide you are interested in.
3. Run the Examples
Each guide includes practical examples. Follow the instructions provided in the guide to execute the examples in your Kubernetes environment.
4. Use the Docker Images
This repository also includes Dockerfiles for Kubernetes tools like kubectl, helm, velero, argocd, fluxcd, and eksctl. You can build and use these images as follows:
Build the All-in-One Docker Image:
docker build \
--build-arg KUBECTL_VERSION=<kubectl_version> \
--build-arg HELM_VERSION=<helm_version> \
--build-arg VELERO_VERSION=<velero_version> \
--build-arg ARGOCD_VERSION=<argocd_version> \
--build-arg FLUX_VERSION=<flux_version> \
--build-arg EKSCTL_VERSION=<eksctl_version> \
-t anvesh35/k8s-tools:allinone \
-f dockerfiles/k8s-tools/allinone/Dockerfile .
Run the All-in-One Docker Image:
docker run --rm -it anvesh35/k8s-tools:allinone bash
5. Contribute to the Repository
We welcome contributions! If you find an issue or have an idea for improvement, feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request.
Conclusion
This repository is a one-stop resource for learning Kubernetes with hands-on examples and practical guides. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced user, you will find valuable content to enhance your Kubernetes knowledge and skills.