EKS Mountpoint for Amazon S3 CSI Driver: Complete Implementation Guide
Access Amazon S3 objects with Mountpoint for Amazon S3 CSI driver
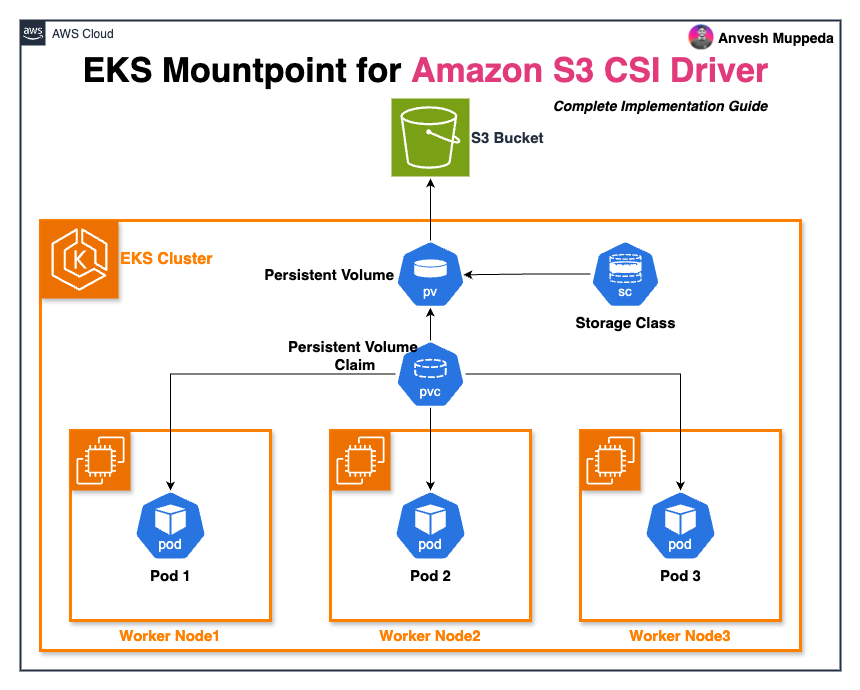
Use the manifest templates to create your own Kubernetes resources which can be used in the examples below.
Use the Cloud Formation templates to create your own AWS resources which can be used in the examples below.
Overview
The Mountpoint for Amazon S3 Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver enables Kubernetes applications to access Amazon S3 objects through a standard file system interface. This integration allows containers running in Amazon EKS and self-managed Kubernetes clusters to interact with S3 buckets as mounted volumes, achieving high aggregate throughput without requiring application code modifications.
Built on the foundation of Mountpoint for Amazon S3, this CSI driver seamlessly bridges the gap between object storage and traditional file system operations, making S3 accessible to applications that expect POSIX-like file operations.
Key Features
- High Performance: Optimized for high aggregate throughput workloads
- Zero Code Changes: Applications can use S3 without modification
- Native Integration: Seamless integration with Kubernetes storage primitives
- Static Provisioning: Works with existing S3 buckets
- Multi-Mount Support: ReadWriteMany and ReadOnlyMany access modes
Prerequisites
Before implementing the Mountpoint S3 CSI driver, ensure you have:
- EKS Cluster: A running Amazon EKS cluster
- IAM OIDC Provider: An existing AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider for your cluster
- AWS CLI: Version 2.12.3 or later installed and configured
- kubectl: Command-line tool installed (version compatible with your cluster)
- S3 Buckets: Pre-existing S3 buckets for static provisioning
Important Considerations and Limitations
Platform Compatibility
- Windows Containers: Not supported with Windows-based container images
- EKS Hybrid Nodes: Not compatible with Amazon EKS Hybrid Nodes
- AWS Fargate: Not supported on Fargate (EC2-based containers only)
Provisioning Limitations
- Static Provisioning Only: Dynamic provisioning and automatic bucket creation are not supported
- Existing Buckets Required: You must specify an existing S3 bucket in the
bucketNamefield
File System Behavior
- Limited POSIX Support: Not all POSIX file system features are available
- Performance Characteristics: Optimized for throughput rather than low-latency operations
Implementation Steps
Note:
Use this CloudFormation template./cloudformation/eks-s3-csi-driver-setup.yaml
to create an EKS cluster including the Mountpoint S3 CSI Driver setup.
Step 1: Create IAM Role and Service Account
The Mountpoint S3 CSI driver requires specific IAM permissions to interact with S3 buckets. Create an IAM role with the necessary permissions:
Using eksctl (Recommended)
# Set environment variables
export CLUSTER_NAME=my-cluster
export REGION=us-west-2
export ROLE_NAME=AmazonEKS_S3_CSI_DriverRole
export POLICY_ARN=arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonS3FullAccess
# Create IAM service account with attached policy
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--name s3-csi-driver-sa \
--namespace kube-system \
--cluster $CLUSTER_NAME \
--attach-policy-arn $POLICY_ARN \
--approve \
--role-name $ROLE_NAME \
--region $REGION \
--role-only
Custom IAM Policy (Production Recommended)
For production environments, create a custom IAM policy with minimum required permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name/*"
]
}
]
}
Step 2: Install the Mountpoint S3 CSI Driver
Install the driver as an Amazon EKS add-on using the AWS CLI:
# Replace with your actual values
export CLUSTER_NAME=my-cluster
export ACCOUNT_ID=111122223333
export ROLE_NAME=AmazonEKS_S3_CSI_DriverRole
# Install the add-on
aws eks create-addon \
--cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME \
--addon-name aws-mountpoint-s3-csi-driver \
--service-account-role-arn arn:aws:iam::$ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ROLE_NAME
Verify Installation
# Check add-on status
aws eks describe-addon \
--cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME \
--addon-name aws-mountpoint-s3-csi-driver
# Verify driver pods are running
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep s3-csi
Practical Implementation Examples
Example 1: Basic Static Provisioning
This example demonstrates mounting a single S3 bucket to a pod:
static_provisioning.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: s3-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1200Gi # Required but ignored for S3
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany # Supports ReadWriteMany/ReadOnlyMany
storageClassName: "" # Required for static provisioning
claimRef:
namespace: default
name: s3-pvc
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- region us-east-1
- prefix some-s3-prefix/ # Optional: mount specific prefix
csi:
driver: s3.csi.aws.com
volumeHandle: s3-csi-driver-volume # Must be unique
volumeAttributes:
bucketName: mountpoint-s3-csi-driver-testing-bucket # Replace with your bucket name
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: s3-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
resources:
requests:
storage: 1200Gi # Required but ignored
volumeName: s3-pv
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: s3-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: ubuntu
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args:
- "-c"
- "echo 'Hello from the container!' >> /data/$(date -u).txt; tail -f /dev/null"
volumeMounts:
- name: persistent-storage
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: s3-pvc
Deploy and Verify:
# Deploy the resources
kubectl apply -f static_provisioning.yaml
# Verify deployment
kubectl get pv,pvc,pods
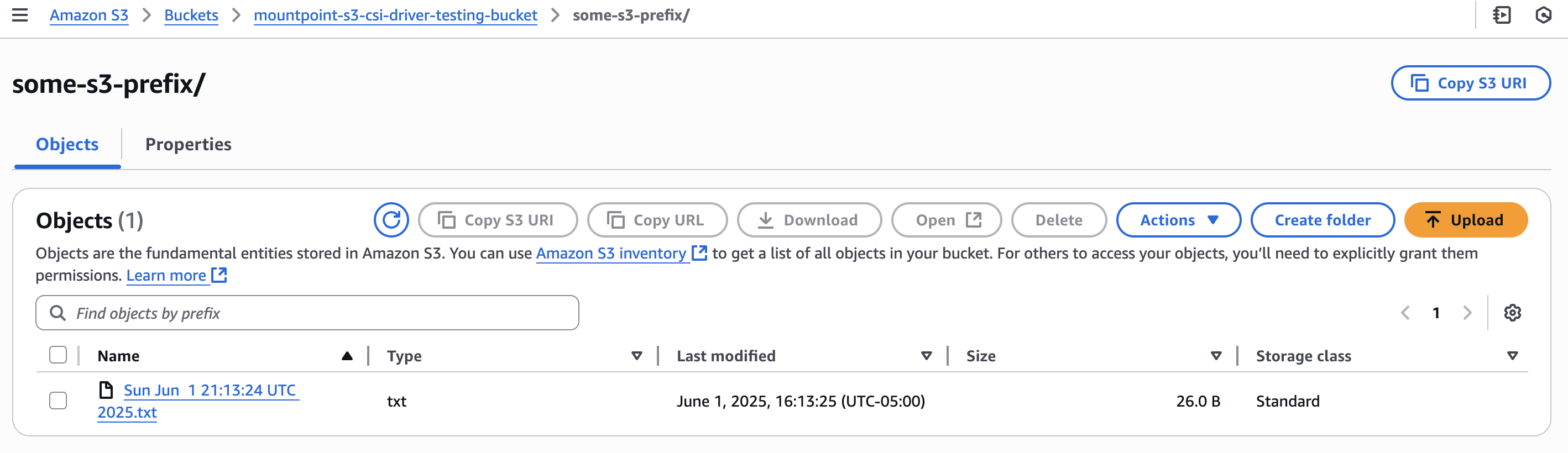
# Check if file was created in S3
> aws s3 ls s3://mountpoint-s3-csi-driver-testing-bucket/some-s3-prefix/
2025-06-01 16:13:25 26 Sun Jun 1 21:13:24 UTC 2025.txt
# Cleanup
kubectl delete -f static_provisioning.yaml
Example 2: Multiple S3 Buckets in One Pod
This example shows how to mount multiple S3 buckets to a single pod:
multiple_buckets_one_pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: s3-pv-bucket1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1200Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
claimRef:
namespace: default
name: s3-pvc-bucket1
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- region us-west-2
csi:
driver: s3.csi.aws.com
volumeHandle: s3-csi-driver-volume-1
volumeAttributes:
bucketName: mountpoint-s3-csi-driver-testing-bucket-1 # Replace with your bucket name
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: s3-pvc-bucket1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
resources:
requests:
storage: 1200Gi
volumeName: s3-pv-bucket1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: s3-pv-bucket2
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1200Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
claimRef:
namespace: default
name: s3-pvc-bucket2
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- region us-west-2
csi:
driver: s3.csi.aws.com
volumeHandle: s3-csi-driver-volume-2
volumeAttributes:
bucketName: mountpoint-s3-csi-driver-testing-bucket-2 # Replace with your bucket name
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: s3-pvc-bucket2
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
resources:
requests:
storage: 1200Gi
volumeName: s3-pv-bucket2
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: s3-multi-bucket-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: ubuntu
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args:
- "-c"
- |
echo 'Data for bucket 1' >> /data1/$(date -u).txt
echo 'Data for bucket 2' >> /data2/$(date -u).txt
tail -f /dev/null
volumeMounts:
- name: storage-bucket1
mountPath: /data1
- name: storage-bucket2
mountPath: /data2
volumes:
- name: storage-bucket1
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: s3-pvc-bucket1
- name: storage-bucket2
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: s3-pvc-bucket2
Bucket 1
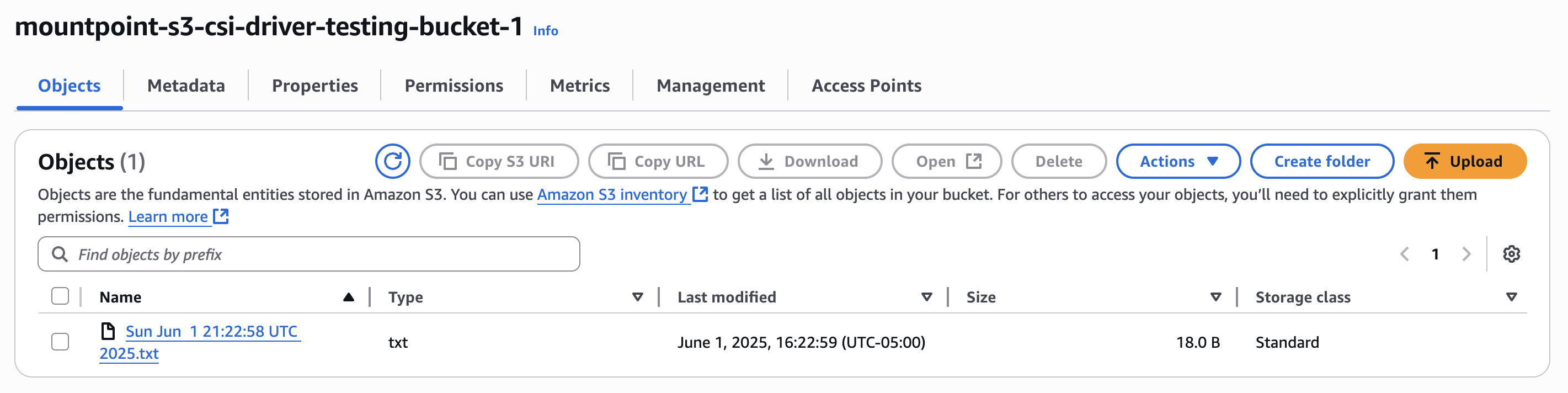
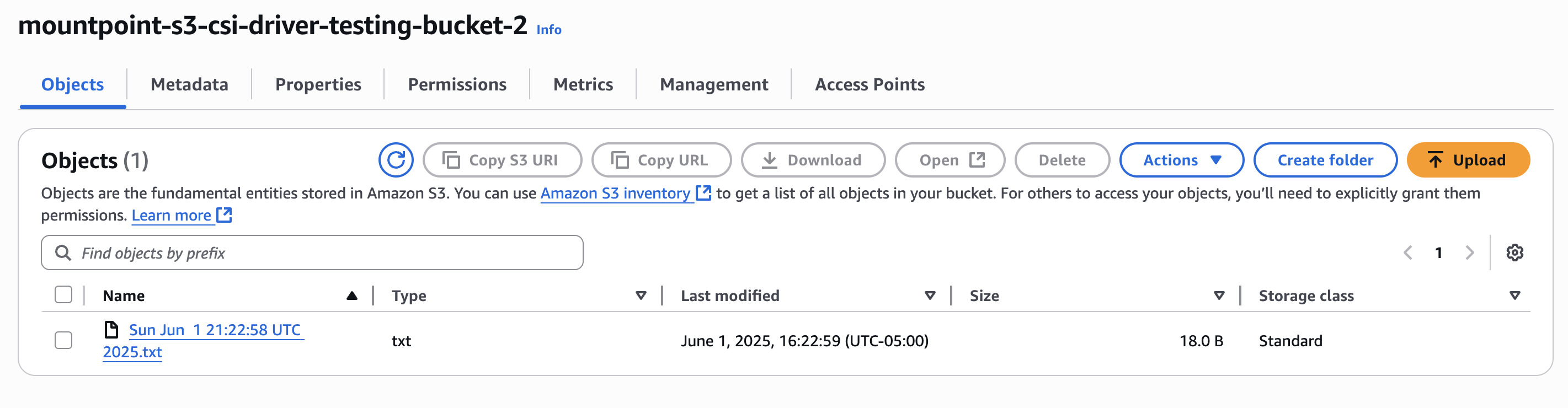
Bucket 2
Example 3: Shared Storage Across Multiple Pods
This example demonstrates multiple pods sharing the same S3 bucket:
multiple_pods_one_bucket.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: s3-shared-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1200Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
claimRef:
namespace: default
name: s3-shared-pvc
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- region us-east-1
csi:
driver: s3.csi.aws.com
volumeHandle: s3-shared-volume
volumeAttributes:
bucketName: mountpoint-s3-csi-driver-testing-bucket # Replace with your bucket name
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: s3-shared-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: ""
resources:
requests:
storage: 1200Gi
volumeName: s3-shared-pv
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: s3-shared-app
labels:
app: s3-shared-app
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: s3-shared-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: s3-shared-app
spec:
containers:
- name: s3-app
image: ubuntu
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args:
- "-c"
- |
POD_NAME=$(hostname)
echo "Hello from pod $POD_NAME at $(date -u)" >> /data/$POD_NAME-$(date -u).txt
tail -f /dev/null
volumeMounts:
- name: shared-storage
mountPath: /data
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumes:
- name: shared-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: s3-shared-pvc
Shared Storage Across Multiple Pods Example
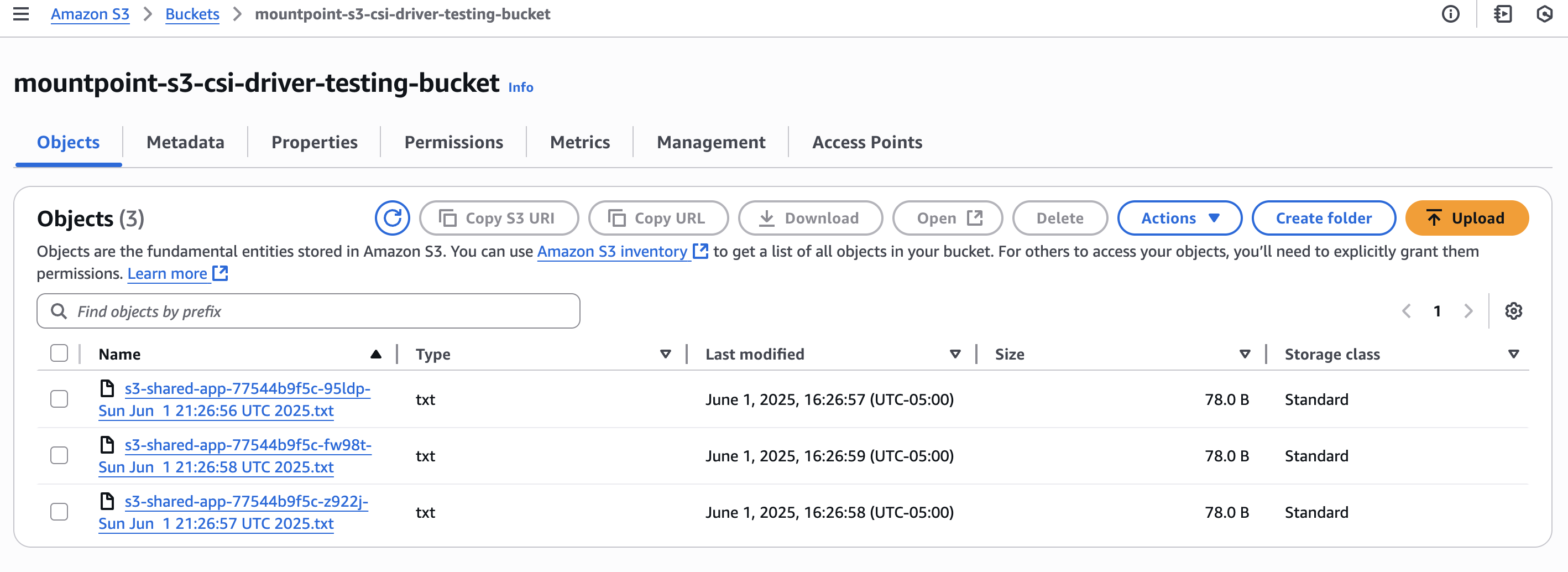
Configuration Options and Mount Options
Available Mount Options
allow-delete: Allows deletion of objectsregion <region>: Specify AWS regionprefix <prefix>: Mount only objects with specific prefixuid <uid>: Set file owner UIDgid <gid>: Set file owner GIDallow-overwrite: Allow overwriting existing files
Performance Tuning
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- region us-west-2
- prefix data/
- cache /tmp/mountpoint-cache
- max-threads 16
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Common Commands for Troubleshooting
# Check driver status
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep s3-csi
# View driver logs
kubectl logs -n kube-system -l app=s3-csi-node
# Describe PV/PVC for issues
kubectl describe pv s3-pv
kubectl describe pvc s3-pvc
# Check mount status inside pod
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- df -h
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- mount | grep s3
Common Issues and Solutions
- Permission Denied: Verify IAM role has correct S3 permissions
- Mount Timeout: Check region configuration and network connectivity
- Bucket Not Found: Ensure bucket exists and is accessible from the cluster region
Use Cases and Benefits
Ideal Use Cases
- Data Analytics: Large-scale data processing workloads
- Machine Learning: Training data access and model storage
- Content Distribution: Serving static content from S3
- Backup and Archive: Application data backup to S3
- Log Aggregation: Centralized logging to S3
Key Benefits
- Cost Effective: Leverage S3's cost-effective storage tiers
- Scalability: Virtually unlimited storage capacity
- Durability: 99.999999999% (11 9's) durability
- Integration: Native Kubernetes storage integration
- Performance: Optimized for high-throughput workloads
Security Best Practices
IAM Policy Recommendations
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only necessary permissions
- Bucket-Specific Policies: Limit access to specific buckets
- Regular Audits: Review and rotate IAM roles periodically
Network Security
# Example network policy for pod-to-S3 communication
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: s3-app-network-policy
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: s3-app
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to: []
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 443
Advanced Configuration
Custom Storage Classes
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: s3-csi-storage
provisioner: s3.csi.aws.com
parameters:
bucketName: my-s3-bucket
region: us-west-2
mountOptions:
- allow-delete
- cache /tmp/s3-cache
Pod Security Context
spec:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 2000
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 3000
containers:
- name: app
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
Cleanup and Maintenance
Removing the Driver
# Remove the EKS add-on
aws eks delete-addon \
--cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME \
--addon-name aws-mountpoint-s3-csi-driver
# Clean up IAM resources
eksctl delete iamserviceaccount \
--name s3-csi-driver-sa \
--namespace kube-system \
--cluster $CLUSTER_NAME
Maintenance Tasks
- Regular Updates: Keep the driver updated to latest version
- Monitoring: Monitor S3 costs and usage patterns
- Performance Review: Regularly assess performance metrics
- Security Audits: Review IAM permissions and access patterns
Additional Resources
- Mountpoint for Amazon S3 CSI Driver GitHub Repository
- Official AWS Documentation
- Mountpoint for Amazon S3 Documentation
- Kubernetes CSI Documentation
- AWS EKS Best Practices Guide
Conclusion
The Mountpoint for Amazon S3 CSI driver provides a powerful solution for integrating S3 storage with Kubernetes workloads. By following this comprehensive guide, you can successfully implement, configure, and manage S3-backed persistent volumes in your EKS environment while maintaining security best practices and optimal performance.