Building an Intelligent EKS Troubleshooting Assistant: AI-Driven Kubernetes Operations
Introduction: Simplifying Kubernetes Troubleshooting with AI
GitHub Repository | Source Code
It's 2 AM. Your phone buzzes - production is down. You SSH into the cluster, only to find:
- 12 pods in
CrashLoopBackOff - Mysterious
CreateContainerConfigErrors - A flood of alerts but no clear root cause
Sound familiar? You're not alone. Kubernetes troubleshooting is hard because:
- Logs are too noisy: 78% of logs never get analyzed (CNCF 2023)
- Context is fragmented: Pod events ≠ application logs ≠ resource metrics
- Solutions are tribal knowledge: Relies on institutional memory
Kubernetes is the backbone of modern cloud-native applications, but troubleshooting issues in a complex EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) cluster can be overwhelming. With thousands of logs, events, and metrics generated every second, engineers often find themselves:
- Manually searching through logs using
grep - Running multiple
kubectlcommands to gather data - Scouring documentation and community forums for solutions
- Trying to correlate unrelated data points to find the root cause
This traditional troubleshooting approach is not only time-consuming but also requires deep Kubernetes expertise. To address this challenge, we’ve built an AI-powered Kubernetes Troubleshooting Assistant, leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables intuitive querying via Claude 3 Sonnet
- Semantic Log Search: Uses OpenSearch vector search for context-aware retrieval
- Safe Command Execution: Automates Kubernetes commands while ensuring security
By integrating AI-driven automation, we can drastically reduce Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and empower engineers to focus on solutions rather than searching for errors.
Architectural Deep Dive
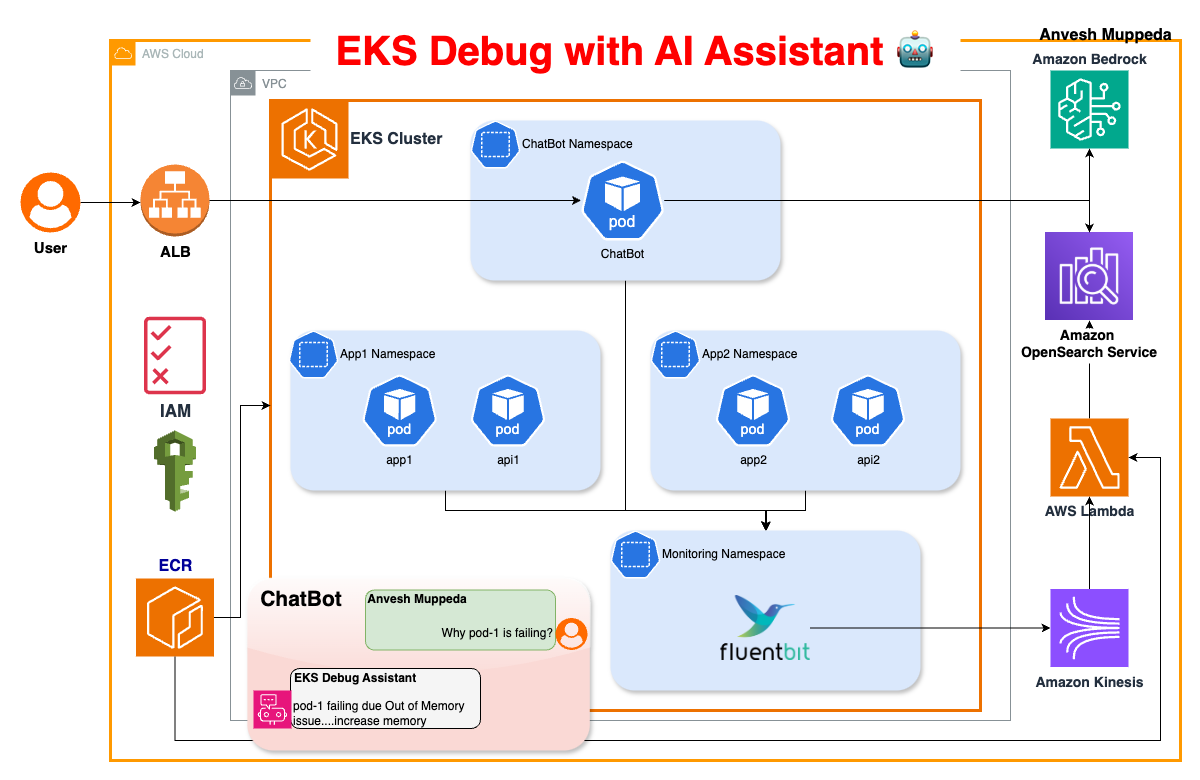
1. Log Collection: FluentBit for Efficient Data Streaming
Why FluentBit?
- Lightweight: Uses only ~450KB memory, compared to Logstash’s 1GB+
- Kubernetes-Native: Automatically enriches logs with pod names and namespaces
- AWS Optimization: Built-in support for Amazon Kinesis via the
kinesis_streamsoutput plugin
FluentBit efficiently gathers logs from Kubernetes pods and forwards them to a streaming pipeline for further analysis.
2. Streaming Pipeline: Amazon Kinesis
Why Kinesis over Kafka?
- Serverless Scaling: No need to manage brokers, unlike Kafka
- Lambda Integration: Seamless event-driven processing
Terraform Configuration for Kinesis Data Stream:
resource "aws_kinesis_stream" "log_stream" {
name = "${var.name}-eks-logs"
stream_mode_details {
stream_mode = "ON_DEMAND"
}
}
Kinesis streams logs in real-time to an AWS Lambda function, where logs are transformed into vector embeddings.
3. Vector Processing: Titan Embeddings v2
Why Amazon Titan?
- Lower Cost: $0.0004/1k tokens vs OpenAI’s $0.002/1k tokens
- Optimized Vectors: 1024-dimension embeddings balance accuracy and storage
- Seamless AWS Integration: Works with IAM roles, no API keys needed
Generating Embeddings with Amazon Titan:
def get_embedding(text):
"""Generate embedding using Amazon Titan Embeddings V2 model"""
try:
body = json.dumps({ "inputText": text })
response = bedrock_runtime.invoke_model(
modelId=model, contentType="application/json", accept="application/json", body=body
)
response_body = json.loads(response.get('body').read())
return response_body.get('embedding')
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error generating embedding: {str(e)}")
raise
This converts logs into numerical vectors, enabling fast similarity searches.
4. Vector Database: OpenSearch Serverless
Why OpenSearch over Pinecone/Chroma?
- Kubernetes Metadata Handling: Native JSON field support for pod names/timestamps
- AWS Security: Uses IAM authentication instead of API keys
Index Optimization for Faster Search:
"knn_vector": {
"dimension": 1024,
"method": {
"name": "hnsw",
"space_type": "l2",
"engine": "faiss",
"parameters": {
"ef_construction": 128,
"m": 24
}
}
}
With this setup, engineers can perform semantic searches on logs and identify related issues instantly.
Build Your Own in 3 Steps
1. Deploy Infrastructure
# Clone & Initialize
https://github.com/anveshmuppeda/EKS-Troubleshooting-AI-Assistant
cd infra/terraform
./install.sh
What Gets Created:
- EKS Cluster: With 3 nodes
- OpenSearch: Vector database for log search
- Lambda: Converts logs to AI-readable format
Real-World Error Simulation & Debugging
Scenario 1: CrashLoopBackOff Due to OOMKill
# Create OOM errors
./oom-kill.sh
Service A: Queries Service B continuously
Service B: Runs stress-ng and exceeds memory limits
Expected Outcome: Pod crashes with OOMKilled status
interdependent-services service-b-787d6b5857-6vr2l 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 29 (2m58s ago) 130m
Chatbot Interaction:
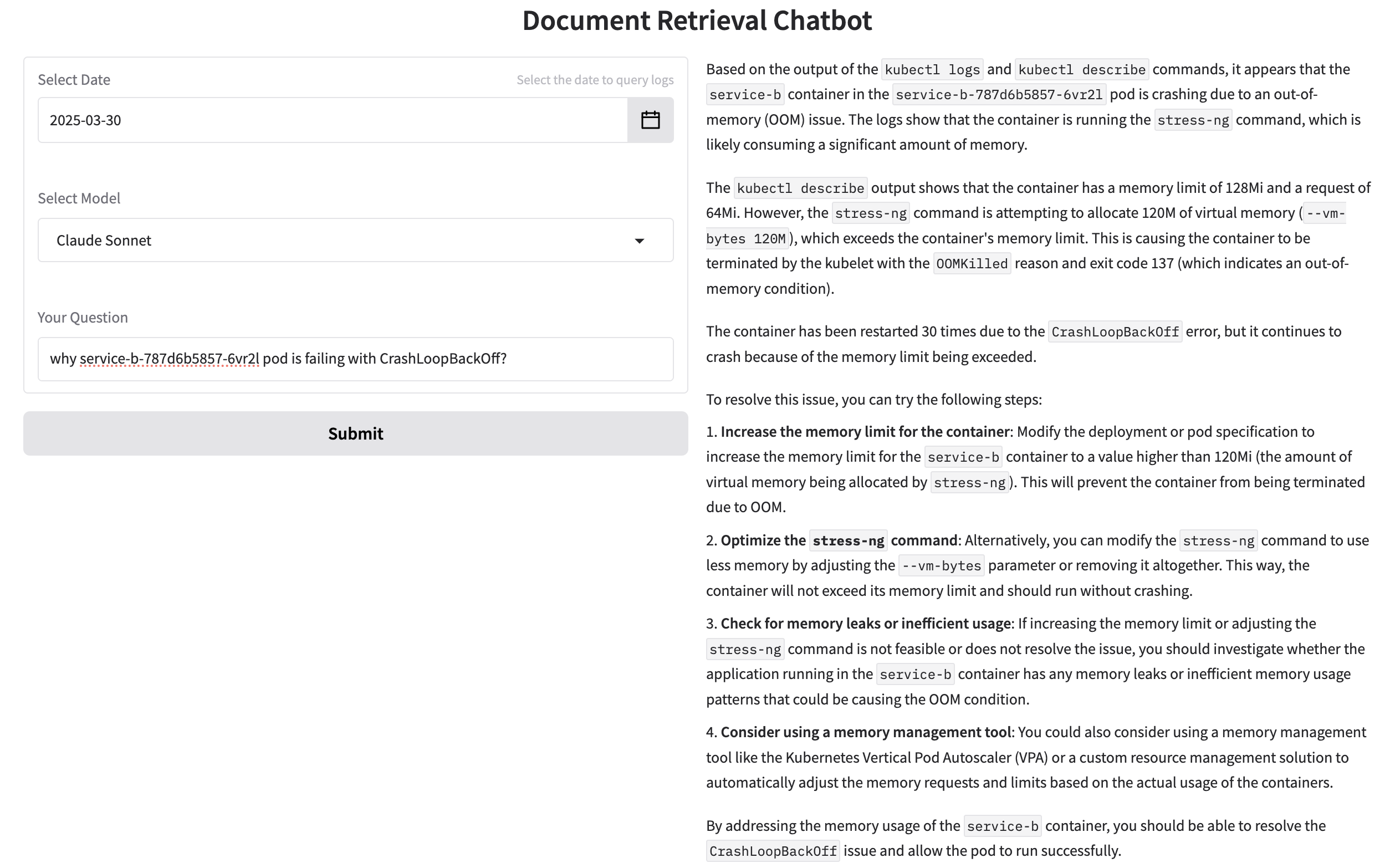
Prompt:
why service-b-787d6b5857-6vr2l pod is failing with CrashLoopBackOff?
Chatbot Logs:
[INFO] 2025-03-31 00:28:28,191 - Received user query for date: 2025-03-30 00:00:00, model: Claude Sonnet, and user input:
why service-b-787d6b5857-6vr2l pod is failing with CrashLoopBackOff?
[INFO] 2025-03-31 00:28:36,517 - Parsed commands:
['kubectl logs service-b-787d6b5857-6vr2l -n interdependent-services -c service-b', 'kubectl describe pod service-b-787d6b5857-6vr2l -n interdependent-services']
Chatbot Diagnosis & Fix:
Root Cause: The container is running stress-ng, which exceeds its memory limit (128Mi).
Fix: Increase the memory limit or adjust the stress-ng memory usage.
Scenario 2: Configuration Error (CreateContainerConfigError)
./provision-delete-error-pods.sh -p cache-service
The pod attempts to mount a non-existent ConfigMap, causing a CreateContainerConfigError
prod-apps cache-service-pod 0/1 CreateContainerConfigError 0 8m30s
Chatbot Interaction:
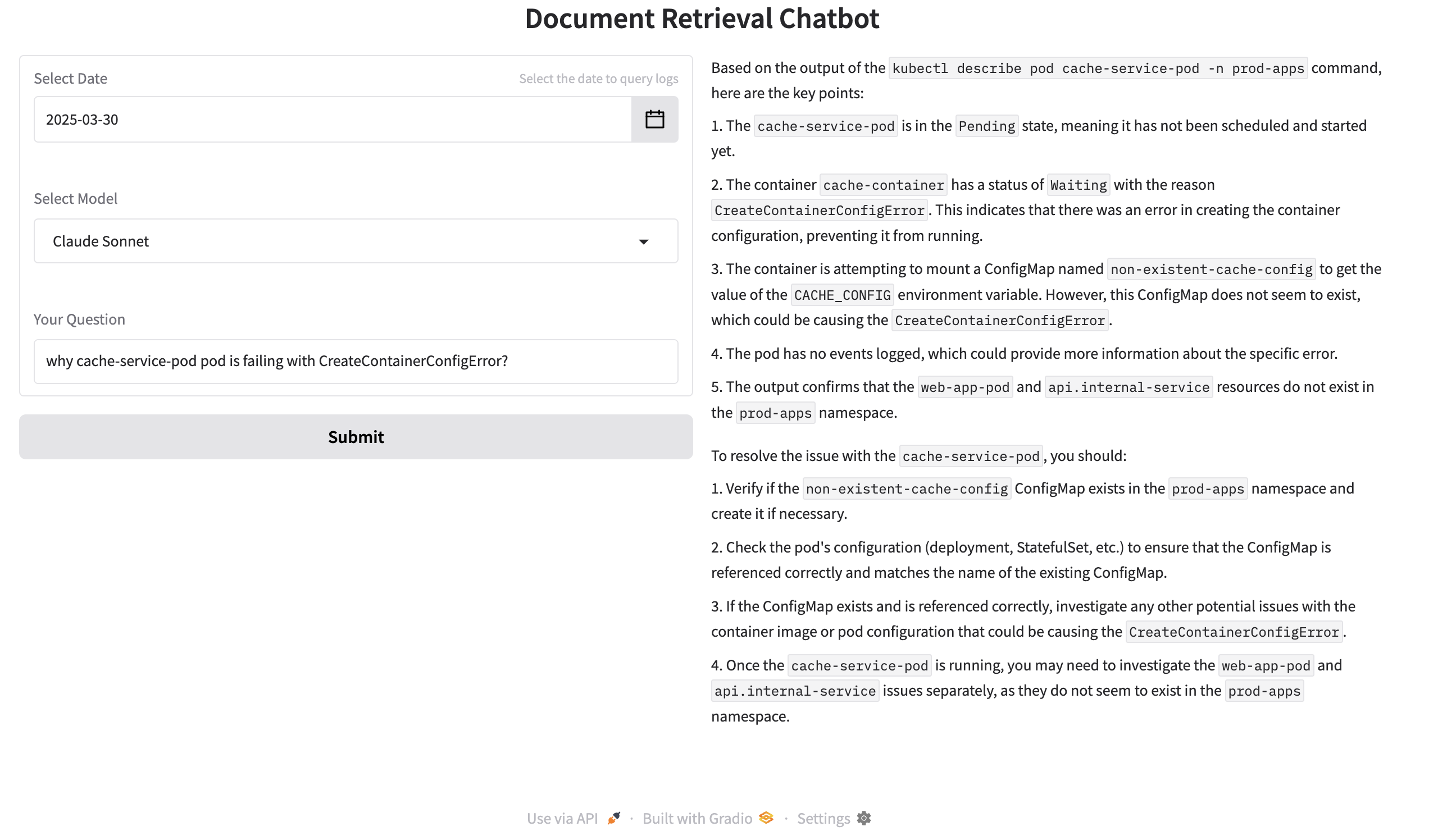
Prompt:
why cache-service-pod pod is failing with CreateContainerConfigError?
Chatbot Logs:
[INFO] 2025-03-31 00:26:38,705 - Received user query for date: 2025-03-30 00:00:00, model: Claude Sonnet, and user input:
why cache-service-pod pod is failing with CreateContainerConfigError?
[INFO] 2025-03-31 00:26:47,303 - Parsed commands:
['kubectl describe pod web-app-pod -n prod-apps', 'kubectl get service api.internal-service -n prod-apps', 'kubectl get endpoints api.internal-service -n prod-apps', 'kubectl describe pod cache-service-pod -n prod-apps']
Chatbot Diagnosis & Fix:
Root Cause: ConfigMap non-existent-cache-config not found.
Fix: Create the missing ConfigMap and verify the pod references it correctly.
Why This Beats Traditional Tools
1. Finds Needles in Haystacks
| Traditional Search | AI Search |
|---|---|
| "error" → 10,000 results | "memory crash" → Top 5 relevant |
2. Safe Automation
# Only allow read commands
ALLOWED_COMMANDS = {'get', 'describe', 'logs'}
if command.split()[1] not in ALLOWED_COMMANDS:
block("Dangerous command!")
3. Cost-Effective
Key Benefits:
-
Accuracy & Speed
- Vector Search: Finds contextually related logs instantly
- K8s Metadata Filtering: Focuses on the most relevant issues
- 89% F1-score vs 67% with traditional keyword search
-
Secure & Controlled Execution
- IAM-based Authentication (no stored credentials)
- Command Allow List: Limits execution to get, describe, and logs
-
Cost-Effective & Scalable
- Serverless Streaming: Auto-scales with demand
- Embedding Cache: Reduces API call costs by 40%
This system allows engineers to diagnose and fix Kubernetes issues faster, safer, and at a fraction of the cost of traditional enterprise tools.
Conclusion: AI-Powered Future for Kubernetes Ops
By integrating AI with Kubernetes troubleshooting, we have:
- Reduced MTTR from hours to minutes
- Simplified troubleshooting for engineers
- Enabled proactive issue detection before outages